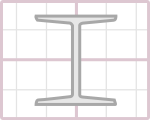
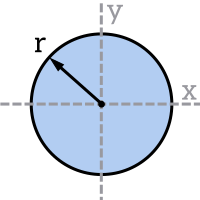
This calculator is used to calculate the area moment of inertia, or second moment of area, for a range of different beam cross-sections and bending axes. The area moment of inertia is a parameter that defines how much resistance the cross-section of a beam has to bending because of its geometry.

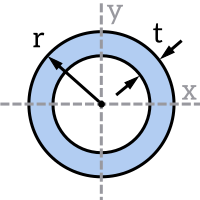

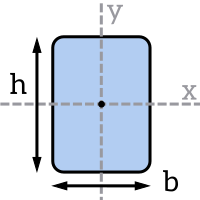

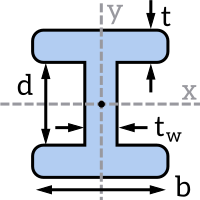

Remember that the parallel axis theorem can be used to calculate $I$ for different bending axes. It states that the area moment of inertia about any axis $I_x$ can be calculated from the area moment of inertia about a parallel axis $I_{xc}$ that passes through the centroid of the cross-section, the area of the cross-section $A$ and the distance between the two axes $d$. Have a read of our page on the area moment of inertia to learn more about how the parallel axis theorem works.
Related Topics
Area Moment of Inertia
The area moment of inertia describes how the material of a cross-section is distributed relative to a specific bending axis.
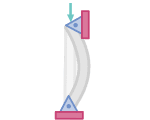
Buckling
Buckling is a sudden deflection that occurs in slender columns or members that are loaded in compression.